Fundamental measures
This activity includes several activities: manipulation of cold molecules, study of antimatter with collaborations at CERN, and measurement of the electric dipole moment of the electron

The experiment deals with the cooling of the internal and external degrees of freedom of a BaF beam. The achievements and perspectives converge towards the objective of obtaining a cold sample of molecules. The aim is to optimize the number of molecules and to control their movement in order to carry out precision measurements (which could be facilitated by the installation of a frequency comb and the arrival of the reference signal REFIMEVE) on the P and CP violation effects for which the BaF molecule is known to have a good sensitivity (dipole of the electron or parity violation effects in the nucleus).
Following the installation of the electrostatic decelerator, the immediate next step in the experiment will be to study neutralization, i.e. electron capture by BaF+ ions. For this, a jet of of cesium atoms promoted to a Rydberg state (Cs* ) will provide a source of cold electrons. The study of BaF+ /Cs* interactions will be the focus of our work: the aim will be to understand the mechanism and efficiency of charge transfer, and identifying in which final states BaF neutralizes itself. Finally, we also intend to use a negative ionic intermediate BaF– , more precisely a dipolar anion, for which the formation and neutralization will require specific studies.
For this ongoing and future work, we will develop new analytical tools (in in particular velocity imaging -VMI and a pulsed laser with optimized spectral linewidth at the Fourier limit)
The activity in antimatter was carried out within AEgIS (Antihydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy) collaboration at CERN and continues via several collaborations:
1 – With Antoine Camper and Norwegian colleagues around the cooling of Ps and antihydrogen with the construction of incoherent nanosecond or coherent picosecond lasers (wavelength 121 nm and 243 nm) (theoretical paper in progress)
2 – With Chloé Malbrunot’s group at CERN concerning the demonstration of laser-stimulated de-excitation of hydrogen and antihydrogen atoms from their Rydberg states, as well as on the improvement of trapping and cooling in particular with a pulsed injected laser fabricated at LAC
Towards an Electric Dipole Moment (EDM)
with atoms and molecules in Matrix (EDMMA)


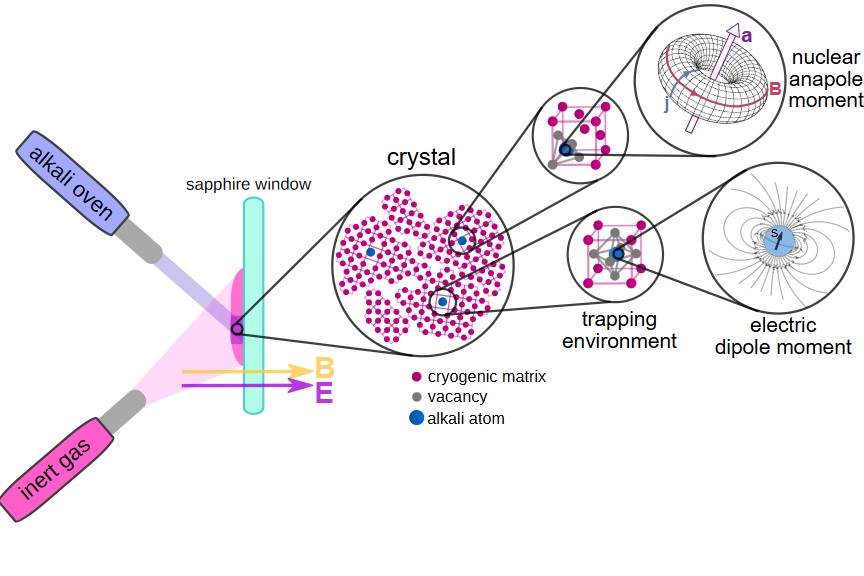
In our project, we work towards tests of fundamental symmetries in atomic systems. A violation of these would indicate the existence of new elementary particles beyond the standard model.
For our experiment, we use the method of matrix isolation spectroscopy: We deposit unreactive gases at such cold temperatures that they freeze into a crystal structure. Inside these crystals, we then dope Alkali atoms, on which we perform various kinds of spectroscopy.
With this, we want to study different properties of this system to perform a measurement of the electron electric dipole moment (eEDM) in the future. This property measures in some sense how round electrons are and is directly linked to symmetry-breaking interactions in models of new physics.

- Hans LIGNIER
hans.lignier@universite-paris-saclay.fr
- Daniel COMPARAT
daniel.comparat@universite-paris-saclay.fr
- Bruno VIARIS
bruno.viaris@universite-paris-saclay.fr
- Thomas BATTARD
thomas.battard@universite-paris-saclay.fr
- Sebastian LAHS
sebastian.lahs@universite-paris-saclay.fr
